
AI Coding Best Practices: A Framework for Human-AI Collaboration
· 667 words · 4 minutes reading time AI Architecture DevOps
"The future of programming is not about replacing developers but augmenting their capabilities. The key is establishing a framework where humans remain in control while leveraging AI's strengths."
The rise of AI coding assistants like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT has sparked both excitement and concern in the development community. While these tools can dramatically accelerate coding tasks, using them without a structured approach can lead to architectural chaos, inconsistent code quality, and a loss of project control.
This article presents a systematic framework for human-AI collaboration in software development, ensuring you maintain architectural control while maximizing AI's potential.
Framework Overview🔗
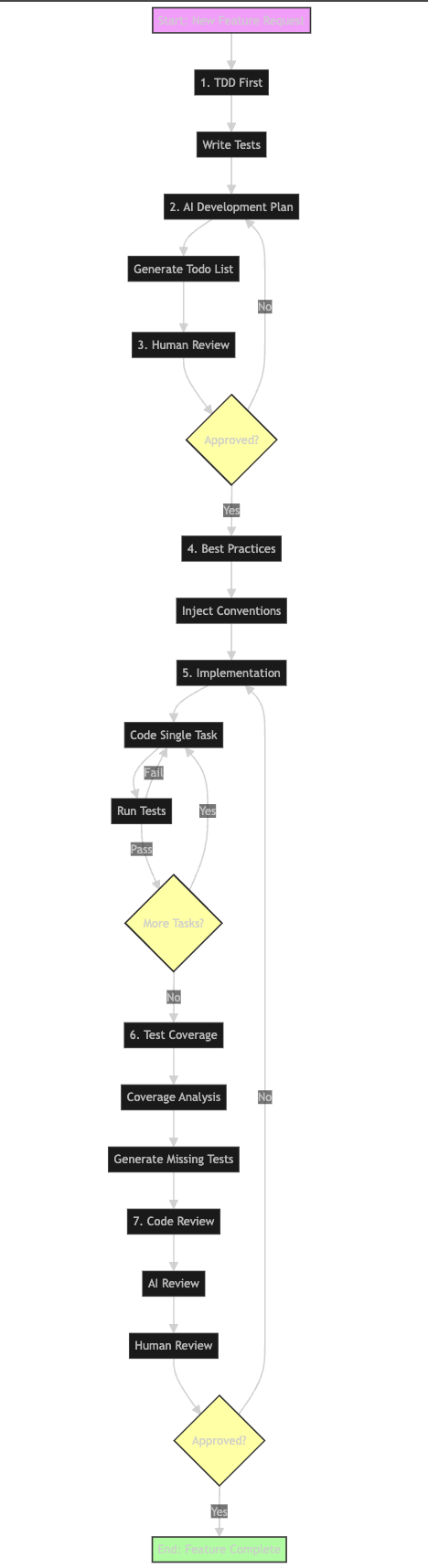
The Challenge: Why AI Coding Needs Structure🔗
Uncontrolled AI coding assistance typically leads to several issues:
- Divergence from Business Goals: AI may optimize for code elegance rather than business requirements
- Architectural Inconsistency: Generated code may not align with project conventions
- Testing Gaps: Critical edge cases and error handling often get overlooked
- Loss of Control: Blurred lines between human and AI responsibilities
- Code Bloat: Generation of unnecessary or redundant code that adds complexity without value
- Code Regression: Potential deterioration or accidental deletion of well-functioning code
These challenges underscore the need for a structured approach to AI-assisted development.
A Framework for Controlled AI Collaboration🔗
Let's explore a structured approach that addresses these challenges while maximizing AI's benefits.
1. Test-Driven Development (TDD) First🔗
Start with tests before any implementation. This approach:
- Clarifies requirements for both you and the AI
- Ensures verifiable outcomes
- Maintains focus on business logic
Example prompt for AI:
Based on these RSpec tests, implement the Rails controller logic:
describe UsersController do
describe 'POST #create' do
it 'creates a new user with valid parameters' do
# test code
end
end
end
2. AI-Generated Development Plan🔗
Have AI create a structured todo list before implementation:
- Break down features into discrete tasks
- Identify dependencies and components
- Plan the implementation sequence
Example prompt:
Given this feature description, create a todo list including:
- Required classes/modules
- Function signatures
- Database changes
- API endpoints
Do not write code yet - wait for my review.
3. Human Review and Approval🔗
Review and modify the AI's plan:
- Align with architectural vision
- Remove unnecessary components
- Confirm implementation approach
- Set clear boundaries
This step is crucial for maintaining control over the project's direction.
4. Inject Best Practices and Conventions🔗
Before coding begins, explicitly provide:
- Project coding standards
- Framework conventions
- Architectural patterns
- Directory structure
- Naming conventions
- Authorization patterns
Example prompt:
You are a senior Rails engineer familiar with:
- Service objects pattern
- Policy-based authorization
- dry-rb gems
Follow these conventions:
[list conventions]
5. Incremental Implementation🔗
Implement one task at a time:
- Generate code for a single component
- Run tests immediately
- Discuss design decisions when needed
- Maintain continuous feedback loop
6. AI-Assisted Test Coverage🔗
Use AI to enhance test coverage:
- Run coverage tools (SimpleCov, pytest-cov)
- Generate tests for uncovered paths
- Ensure edge cases are handled
Example prompt:
Here's the SimpleCov report showing uncovered lines.
Generate appropriate tests for these scenarios:
[uncovered scenarios]
7. Dual-Layer Code Review🔗
Implement a two-stage review process:
-
AI Review:
- Check naming conventions
- Identify code smells
- Spot potential bugs
- Suggest refactoring opportunities
-
Human Review:
- Verify business logic
- Ensure architectural alignment
- Final approval and merge
Control Matrix: Human vs AI Responsibilities🔗
| Stage | Human Lead | AI Assistant |
|---|---|---|
| Writing Prompts | ✅ | |
| Generating Todos | ✅ | |
| Plan Review | ✅ | |
| Best Practices Input | ✅ | |
| Implementation | ✅ (control) | ✅ (execution) |
| Test Enhancement | ✅ | ✅ |
| Coverage Review | ✅ | ✅ |
| Initial Code Review | ✅ | |
| Final Review | ✅ |
Benefits of This Framework🔗
- Maintained Control: Humans drive architectural decisions and project direction
- Consistent Quality: Standardized approach ensures reliable output
- Efficient Collaboration: Clear boundaries maximize both human and AI strengths
- Comprehensive Testing: Structured approach to quality assurance
- Scalable Process: Framework adapts to different project sizes and technologies
Implementation Tips🔗
- Document Your Framework: Create a team guide for AI collaboration
- Start Small: Begin with smaller features to refine the process
- Iterate: Adjust the framework based on team feedback
- Track Metrics: Monitor the impact on development speed and code quality
- Share Learning: Document successful prompts and patterns
Conclusion🔗
The key to successful AI-assisted development isn't just about having powerful tools—it's about having a structured framework that maintains human control while leveraging AI's capabilities. This approach ensures that AI remains an assistant rather than taking the lead, resulting in higher quality code that aligns with your project's architecture and business goals.
Remember: AI should augment your development process, not replace your architectural judgment. With this framework, you can confidently integrate AI tools into your workflow while maintaining control over your codebase's quality and direction.